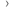A trial of selumetinib with dacarbazine for advanced melanoma in people with a BRAF gene fault
Cancer type:
Status:
Phase:
This trial looked at a drug called selumetinib alongside dacarbazine for people with melanoma that has spread to another part of the body. This is called advanced melanoma. It was for people whose melanoma cells have a change ( ) in a
) in a  called BRAF.
called BRAF.
More about this trial
Doctors may treat advanced melanoma with chemotherapy. They usually use a drug called dacarbazine. But researchers are looking at ways to improve treatment. In this trial they looked at a drug called selumetinib alongside dacarbazine.
Selumetinib is a type of biological therapy called a cancer growth blocker. It stops signals that cancer cells use to divide and grow.
The researchers compared selumetinib and dacarbazine with dacarbazine alone. The aims of the trial were to find out
- If selumetinib and dacarbazine together worked better than dacarbazine alone for people with advanced melanoma whose melanoma cells have the BRAF gene mutation
- More about the side effects
Summary of results
The trial team found that having selumetinib alongside dacarbazine extended the length of time before the cancer started to get worse by about 2½ months.
91 people who hadn’t had any other treatment for advanced melanoma took part in this trial.
- 45 had dacarbazine and selumetinib
- 46 had dacarbazine and a dummy drug (
placebo) 
The researchers looked at the average length of time people lived without any signs of their cancer getting worse. Researchers call this progression free survival. They found it was
- Just over 5½ months for people who had dacarbazine and selumetinib
- 3 months for people who had dacarbazine
The researchers also looked at how long people lived on average after treatment. Doctors call this overall survival. They found that the group who had dacarbazine and selumetinib lived a little longer, but the difference between the 2 groups could have happened by chance (the results were not  )
)
People in the selumetinib group had more problems with feeling or being sick, a skin rash, diarrhoea and swelling of their hands and feet.
Despite causing more side effects, the trial team concluded that having dacarbazine alongside selumetinib improved progression free survival for people whose melanoma cells have a change in a gene called BRAF. But it did not affect the average length of time people lived after treatment (overall survival).
We have based this summary on information from the team who ran the trial. The information they sent us has been reviewed by independent specialists ( ) and published in a medical journal. The figures we quote above were provided by the trial team. We have not analysed the data ourselves.
) and published in a medical journal. The figures we quote above were provided by the trial team. We have not analysed the data ourselves.
Recruitment start:
Recruitment end:
How to join a clinical trial
Please note: In order to join a trial you will need to discuss it with your doctor, unless otherwise specified.
Chief Investigator
Prof Mark Middleton
Supported by
AstraZeneca
Experimental Cancer Medicine Centre (ECMC)
NIHR Clinical Research Network: Cancer
If you have questions about the trial please contact our cancer information nurses
Freephone 0808 800 4040