Sun, UV and cancer
Sunburn doesn’t just happen abroad or when it’s hot outside. The sun can be strong enough in the UK to damage your skin from mid-March to mid-October, even if it’s cold or cloudy. Clouds block some UV, but over 90% of UV rays can still pass through cloud and cause sunburn.
Being aware of when the sun is strong and knowing how your skin reacts to the sun can help you avoid skin damage and sunburn.
Too much UV radiation from the sun is the main cause of skin cancer in the UK. Up to 9 in 10 cases of melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer, could be prevented by enjoying the sun safely. So, whether you’re working outside, doing the gardening or sitting in the park, it’s important to be safe in the sun.
In the UK or abroad, when the sun is strong, think about protecting your skin by:
Spending time in the shade – take a break under umbrellas, parasols or trees, or go inside, especially between 11am and 3pm in the UK.
Covering up – wear loose clothing that covers your shoulders. The more skin that’s covered, the better. Pair with a wide brimmed hat and UV protection sunglasses.
Using sunscreen – on bits that you can’t cover with clothes or shade. Apply sunscreen with at least SPF 30 and 4 or 5 stars regularly and generously.
Find out more about how to enjoy the sun safely.
In the UK, the sun is often strong enough to cause skin damage between mid-March and mid-October. The sun is strongest in the middle of the day when it’s highest in the sky, which is 11am to 3pm in the UK.
Tools like the UV index and the Shadow Rule can help you work out when you need to protect your skin and follow sun safety advice.
The UV index tells us how strong the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays are. The higher the UV index number, the less time it takes for your skin to become damaged by the sun. So the risk of sunburn is higher.
When the UV index is 3 (moderate) or above, the sun is strong enough to cause damage for some skin types so think about protecting your skin, especially if you burn easily.
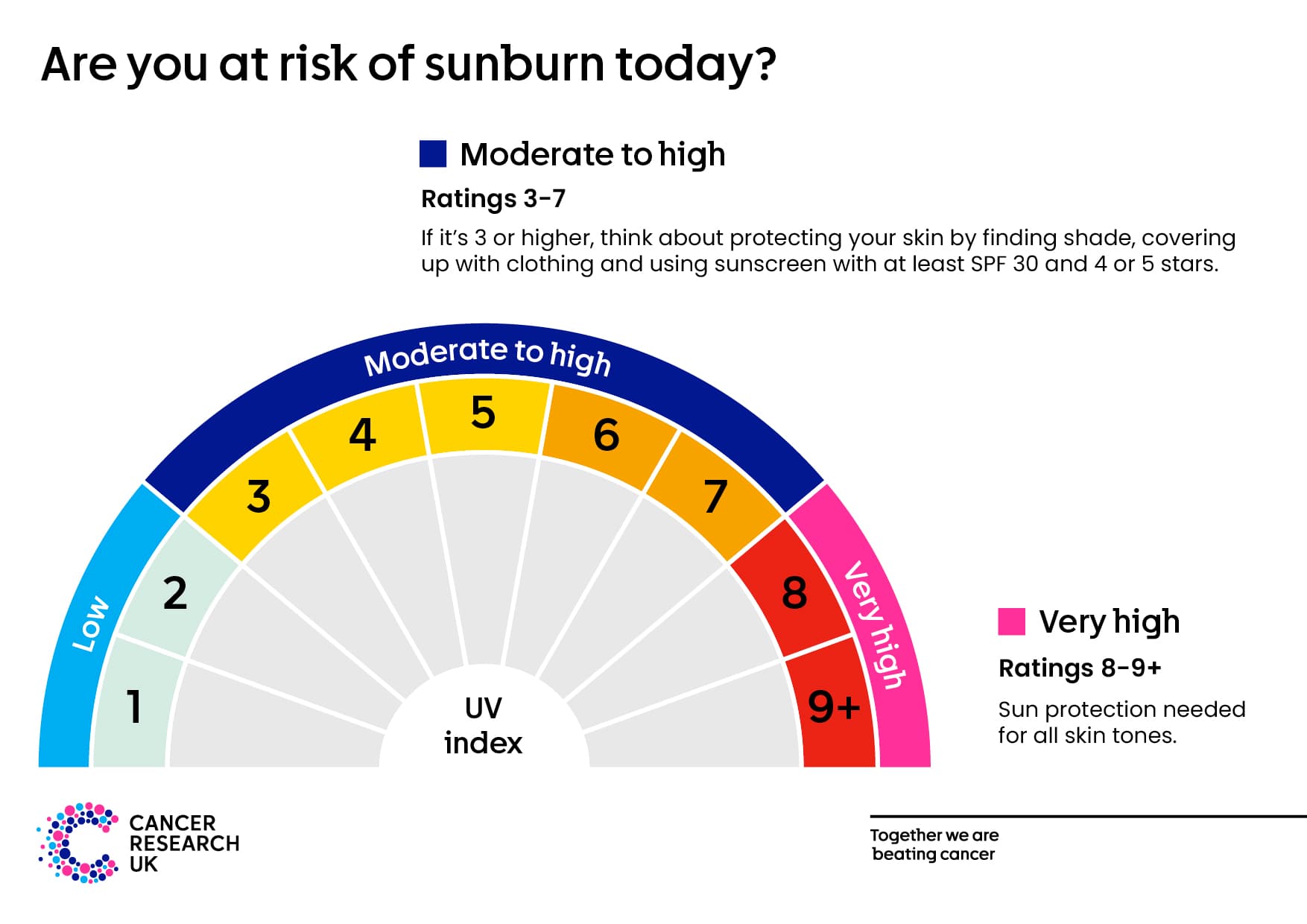
UV 1-2 – Low levels. No sun protection needed.
UV 3-7 – Moderate to high levels. Be sun safe and consider protecting your skin.
UV 8-9+ – Very high levels. Everyone should protect their skin.
The strength of the sun’s UV rays varies by location. Near the equator, there are strong UV rays all year round. So whether in the UK or abroad, get into the habit of checking the UV index and protecting your skin when you need to.
You can find the UV index for your area on local TV weather forecasts, by searching online, or checking weather apps on your phone.
Another handy tip to help you work out when the sun is strongest is the ‘Shadow Rule’. It’s simple and it works anywhere in the world. It’s also a fun way to talk to children about enjoying the sun safely.
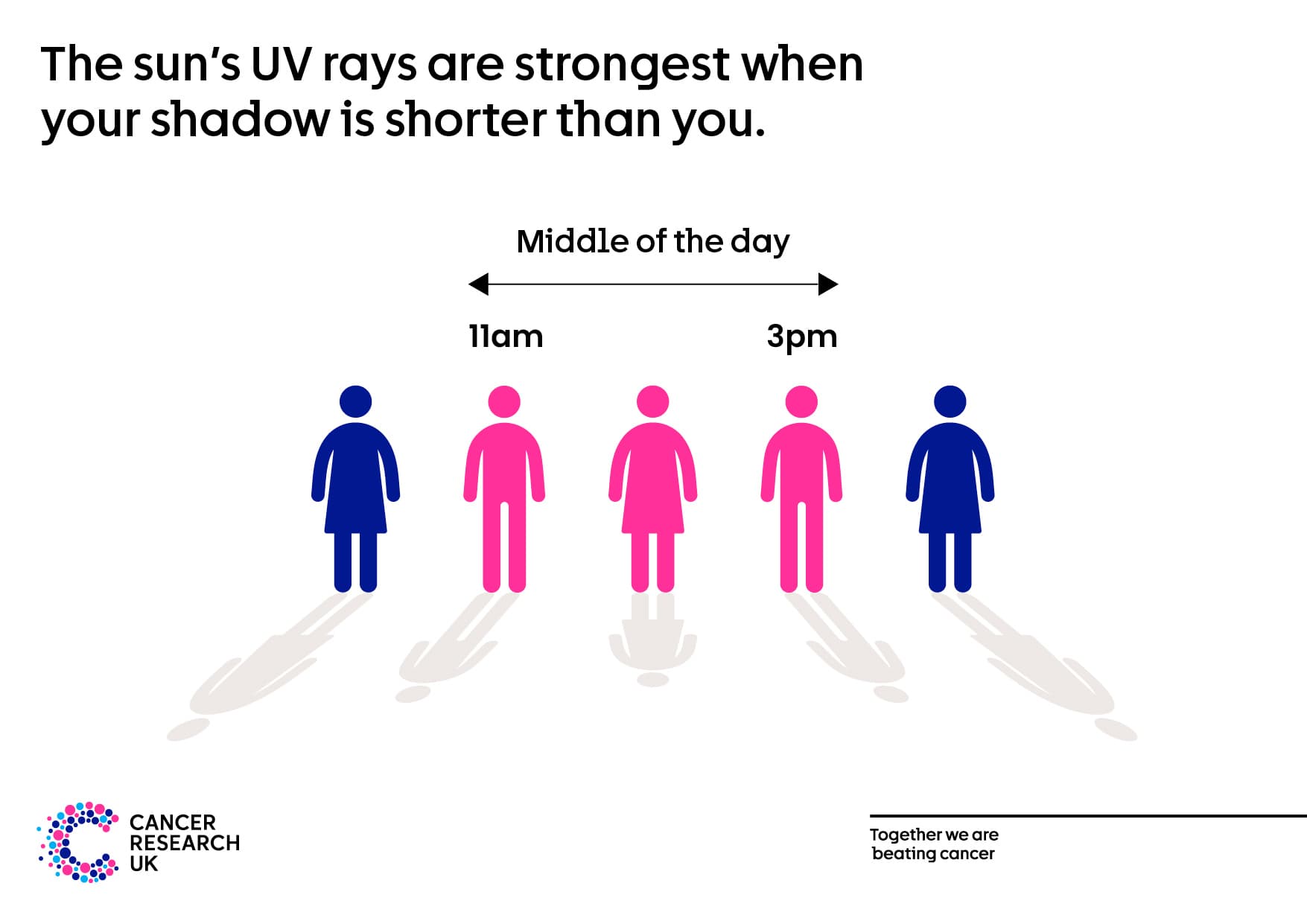
Look at your shadow. If it is shorter than you, this means that the sun’s UV rays are at their strongest – in the UK, this is usually the middle of the day between 11am and 3pm. This is when you’re most likely to burn and need to think about taking extra care to protect your skin, especially if you get sunburnt easily.
Getting sunburnt can increase your risk of skin cancer. Anyone can get sunburn or develop skin cancer, but some people are at a higher risk and need to take more care in the sun.
You should take more care in the sun if you have one or more of the following:
skin that burns easily
a lighter skin tone
light coloured hair or eyes
lots of moles or freckles
a history of sunburn
a personal or family history of skin cancer
You’re the best person to know how your skin reacts to the sun. The more easily you get sunburnt, the more careful you need to be.
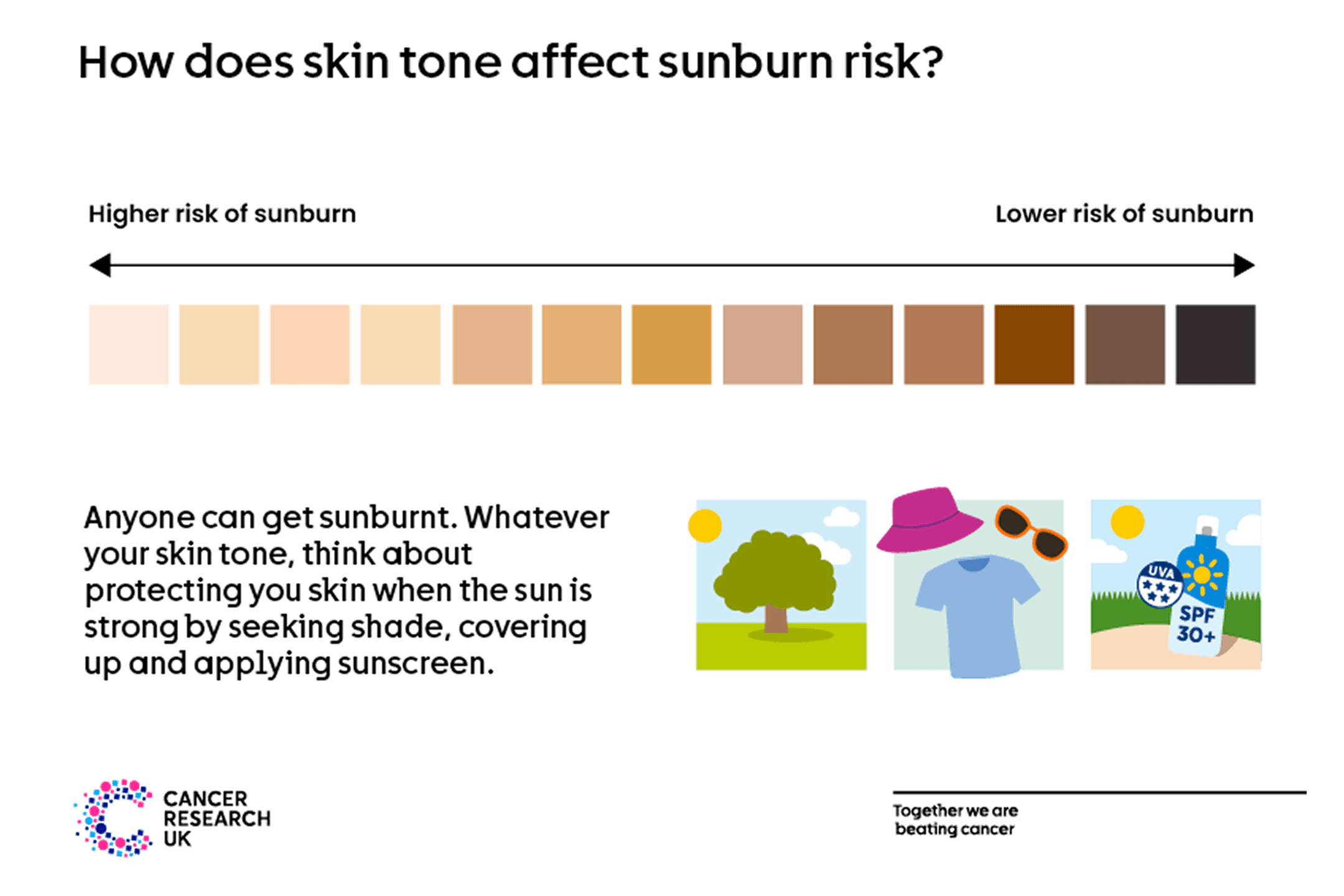
Sunburn doesn’t have to be raw, peeling or blistering. For people with darker skin tones, your skin may feel irritated, tender or itchy. For people with lighter skin tones, it may also go pink or red in the sun.
People with naturally darker skin tones, such as brown or black skin, burn less easily and have a lower risk of skin cancer.
But lower risk doesn’t mean there’s no risk. People with darker skin tones can still get sunburnt. And people of all skin tones can get skin cancer, so it’s important for everyone to think about protecting their skin when the sun is strong.
A bit of sun helps our bodies to produce vitamin D, which is important for things like healthy bones. People with darker skin tones need to spend longer in the sun to produce enough vitamin D, but there’s no need to sunbathe. You can also get vitamin D from your diet or supplements. If you’re worried about your vitamin D levels, talk to your doctor.
Read more about the sun and vitamin D.
If you’ve got more questions about sun safety read our article on common questions and myths about the sun.
Last reviewed: 30 Nov 2023
Next review due: 30 Nov 2026
Questions about cancer? Call freephone 0808 800 40 40 from 9 to 5 - Monday to Friday. Alternatively, you can email us.