Non melanoma skin cancer symptoms
Skin cancers can look very different. They might be:
a spot or sore
a lump
a red or dark patch
itchy, crusty or bleeding
The earlier a skin cancer is diagnosed, the easier it is to treat. So it's important you visit your GP as soon as possible if you notice a change in your skin.
Non melanoma skin cancer tends to develop most often on skin exposed to the sun.
To spot skin cancer early it helps to know how your skin normally looks. That way, you'll notice any changes more easily.
To look at areas you can’t see easily, you could try using a hand held mirror and reflect your skin onto another mirror. Or you could get your partner or a friend to look. This is very important if you're regularly outside in the sun for work or leisure.
You can take a photo of anything that doesn't look quite right. If you can it's a good idea to put a ruler or tape measure next to the abnormal area when you take the photo. This gives you a more accurate idea about its size and can help you tell if it's changing. You can then show these pictures to your doctor.
There are different types of basal cell skin cancers. These include:
nodular basal cell skin cancer
pigmented basal cell skin cancer
morphoeic basal cell skin cancer - also known as sclerosing or infiltrating basal cell skin cancer
superficial basal cell skin cancer
Nodular basal cell cancers can look see through (translucent) and shiny. You can often also see their blood vessels. Sometimes they have a sore (ulcerated) area and it may also have fluid filled sacs (cystic).
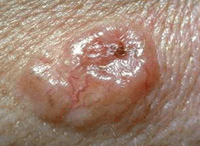
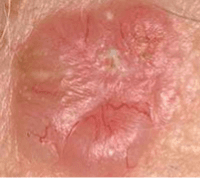
Pigmented basal cell cancers have dark areas, often brown, blue or grey in colour. They can look like warts or sometimes a melanoma.
Read more about melanoma skin cancer
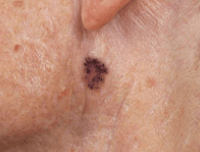
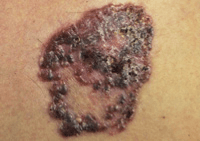
Pronounced mor-fee-ic, this type of basal cell skin cancer may look like a sore area on the skin that doesn’t heal. It might look skin coloured, waxy, like a scar or thickened area of skin that's very slowly getting bigger. You might also see small blood vessels.


Squamous cell skin cancers can vary in how they look. They usually occur on areas of skin exposed to the sun like the scalp or ear.
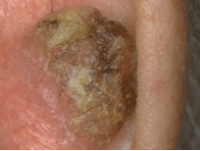

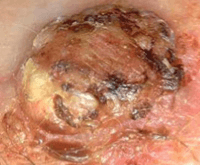
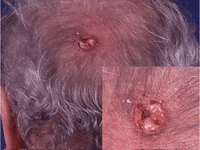
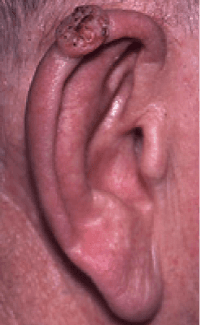
Thanks to Dr Charlotte Proby for her permission and the photography.
Last reviewed: 19 Dec 2022
Next review due: 19 Dec 2025
Symptoms of skin cancer can include: a sore that doesn't heal, an area of skin that looks unusual, red, itchy, bleeds or scabs for more than 4 weeks.
See your GP if you notice a change in your skin that isn't normal for you. Or if you have any of the possible signs and symptoms of skin cancer.
The main test to diagnose skin cancer is to take a sample (biopsy) of the area. There are different types of biopsy.
Non melanoma skin cancer includes basal cell skin cancer, squamous cell skin cancer and other rare types.
Most skin cancers are caused by exposure to the sun. There are some other factors that can increase your risk.
Non melanoma skin cancer includes basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and other rare types. They tend to develop most often on skin that has been exposed to the sun.

About Cancer generously supported by Dangoor Education since 2010. Learn more about Dangoor Education
Search our clinical trials database for all cancer trials and studies recruiting in the UK.
Connect with other people affected by cancer and share your experiences.
Questions about cancer? Call freephone 0808 800 40 40 from 9 to 5 - Monday to Friday. Alternatively, you can email us.