MRI scan
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a type of scan that uses magnetism and radio waves to take pictures of inside the body.
- The scan takes between 15 and 90 minutes.
- You might have one to find out whether you have cancer. It can measure how big it is and whether it has spread. You might also have one to see how well treatment is working.
- It is a safe test. If you have an injection of contrast dye it can cause a headache, dizziness or a warm flushed feeling.
An MRI is a type of scan that creates pictures using magnetism and radio waves. MRI scans produce pictures from angles all around the body and shows up soft tissues very clearly.
MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging. They take between 15 and 90 minutes.
A  operates the scanner and looks after you while you have your scan.
operates the scanner and looks after you while you have your scan.
Why do I need an MRI scan?
An MRI scan can be used to look at most areas of the body and is used to:
-
find a tumour
-
find out how big it is and whether it has spread (stage a cancer)
-
measure blood flow
-
to check how well treatment is working
You might have an injection of a special dye called a  before the scan. This is to help make the scan pictures clearer.
before the scan. This is to help make the scan pictures clearer.
MRI scans are particularly good for:
-
brain tumours
-
primary bone tumours
-
soft tissue sarcomas
-
tumours affecting the spinal cord
-
tumours in the pelvic organs, including prostate, bladder, womb and ovarian tumours
MRI instead of CT scans
In some situations, your doctor may suggest an MRI scan if a CT scan hasn't been able to give all the information they need.
In some cancers, an MRI can be better than CT scans at showing how deeply the tumour has grown into body tissues. It can be particularly useful for showing whether the tissue left behind after treatment is cancer or not.
What to expect when you have an MRI scan
Your appointment letter will list any special instructions. For most MRI scans, there is no special preparation beforehand. But for some, you might have to stop eating a few hours before your test. This depends on which part of the body you are having scanned.
Take your medicines as normal unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
You might need a blood test to check your kidney function. Your MRI team will let you know if you need this.
Preparing for your MRI scan
Before you go to your appointment, or when you arrive, you fill in a safety checklist. This asks about:
- any operations you’ve had
- whether you have any metal implants or other metal in your body
- any allergies you may have
An MRI scan uses strong magnetism which could affect any metal in your body. This includes:
- pacemakers or an implantable defibrillator (to treat abnormal heart rhythms)
- surgical clips, pins or plates
- cochlear implants (for deafness)
- metal fragments anywhere in your body – for example, from an injury, dental fillings and bridges
You may still have an MRI scan if you have some metal in your body. But your doctor and radiographer will decide if it’s safe for you. It’s important to tell the scanner staff about any metal in your body.
Some people feel claustrophobic or closed in when they’re having an MRI scan. Contact the department before your test if you’re likely to feel like this. The hospital staff can take extra care to make sure you’re comfortable and that you understand what’s going on. Your doctor can give you medicine to help you relax if you need to.
An MRI is generally safe during pregnancy. But it is important to tell your doctor or the MRI staff beforehand if you think you’re pregnant. They will discuss the risks and benefits with you.
Having an MRI scan
When you arrive at the department the radiographer explains what will happen and asks you to sign a consent form. This is a good time to ask any questions you may have.
Your radiographer might ask you to change into a hospital gown. You might not have to undress if your clothing doesn’t have any metal, such as zips or clips.
You have to:
- remove any jewellery, including body piercings and your watch
- remove your hair clips
- empty your pockets of coins and keys
You might be able to take a relative or friend into the scanning room with you. But check with the department staff first. Your friend or relative will also need to remove any metal they have on them.
In the scanning room
Your radiographer takes you into the scanning room. The MRI machine is large and shaped like a doughnut.
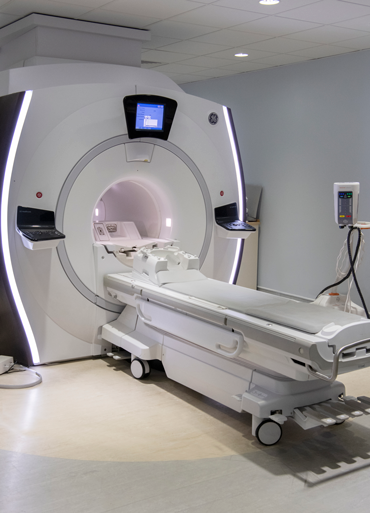
You lie on your back on a couch that can slide into the MRI machine.
You might have an injection of a dye (contrast medium) through a small plastic tube called a cannula into a vein in your arm. This helps to show up your body’s organs more clearly. Some people are allergic to the dye, so your radiographer will check first about any medical conditions or allergies you have.
After the dye injection you may:
- feel sick
- have a headache
- feel warm or flushed
- have a metallic taste in your mouth
- feel a little dizzy
- have a skin rash
These effects are usually mild and last for a short time. Tell your radiographer if you feel unwell at any point during or after your scan.
Once you’re in the right position on the couch, your radiographer leaves the room. They can see you on a TV screen or through a window at all times from the control room. You can talk to each other during the scan, usually through an intercom. You will have a button you can press if you want them to stop the scan immediately if you feel claustrophobic.
You need to lie as still as possible. The scan is painless but it can be uncomfortable to stay still. Tell the radiographer if you're getting stiff and need to move.
The couch moves through the MRI scanner. It takes pictures as you move through it. Your radiographer might ask you to hold your breath at times.
The scanner makes a very loud clanging sound throughout the scan. You wear headphones or earplugs to protect your hearing. You may also be able to listen to music during your scan.
The scan can take between 15 and 90 minutes. It depends on the area that they need to scan and how many images they need.
This 1 minute video shows you what happens when you have an MRI scan.
Voiceover: This is an MRI scanner.
This type of scan uses magnetism to build up a picture of the inside of your body to help your doctor either make a diagnosis and decide what treatment you need or to find out if your treatment is working.
The radiographer makes sure you are lying in the correct position on the couch and explains what will happen.
You need to lie as still as possible.
MRI scans are very noisy so you wear ear plugs or headphones. During the scan you won’t feel anything.
The space you lie in can feel small, if you think you will find it difficult being in a small space, contact the scanning department before your appointment.
The radiographer controls the scan from a separate room but they will be able see and hear you throughout.
Here you can see an example of an MRI scan.
Once the scan is finished you can go home.
After your MRI scan
When the scan is over, your radiographer comes back into the room and lowers the couch so that you can get up.
You usually stay in the department for about 15 minutes after your scan if you've had the dye. This is in case it makes you feel unwell.
Your radiographer removes the cannula from the vein in your arm before you leave.
You should then be able to go home or back to work, and also eat and drink normally.
After having medicine to help you relax
If you’ve had medicine to help you relax (sedation), you need someone to take you home and stay overnight. If you've had sedation, for the next 24 hours, you also shouldn’t:
- drive
- drink alcohol
- operate heavy machinery
- sign any legally binding documents
Possible risks
An MRI is very safe and doesn’t use radiation. Some people can’t have an MRI but the checklist picks this up beforehand. Your doctor and radiographer make sure the benefits of having the test outweigh any possible risks.
Some of the possible risks include:
Bruising and swelling
You might get a small bruise around the area where they put the needle in for the cannula.
There's a risk that the contrast medium will leak outside the vein. This can cause swelling and pain in your arm but it’s rare. Tell your radiographer if you have any swelling or pain. Let your GP know if it doesn’t get better or starts to get worse when you’re at home.
Allergic reaction
An allergic reaction to the contrast medium injection is rare. This most often starts with feeling weak, sweating and difficulty breathing. Tell your radiographer straight away if you feel unwell so they can give you medicine to control the reaction.
Getting your results
You should get your results within 1 or 2 weeks.
Ask your doctor, radiographer, or nurse how long it will take to get them. Contact the doctor who arranged the test if you haven’t heard anything after a couple of weeks.
Waiting for test results can make you anxious. You might have the contact details of a specialist nurse who you can speak to for information and support if you need to. It may also help to talk to a close friend or relative about how you feel.
For information and support, you can call the Cancer Research UK information nurses on freephone 0808 800 4040. The lines are open from 9am to 5pm, Monday to Friday.
More information
We have more information on tests, treatment and support if you have been diagnosed with cancer.



